Sorting Visualizer
Watch sorting algorithms work in real-time. See every comparison and swap as eight different algorithms race to sort the same array.
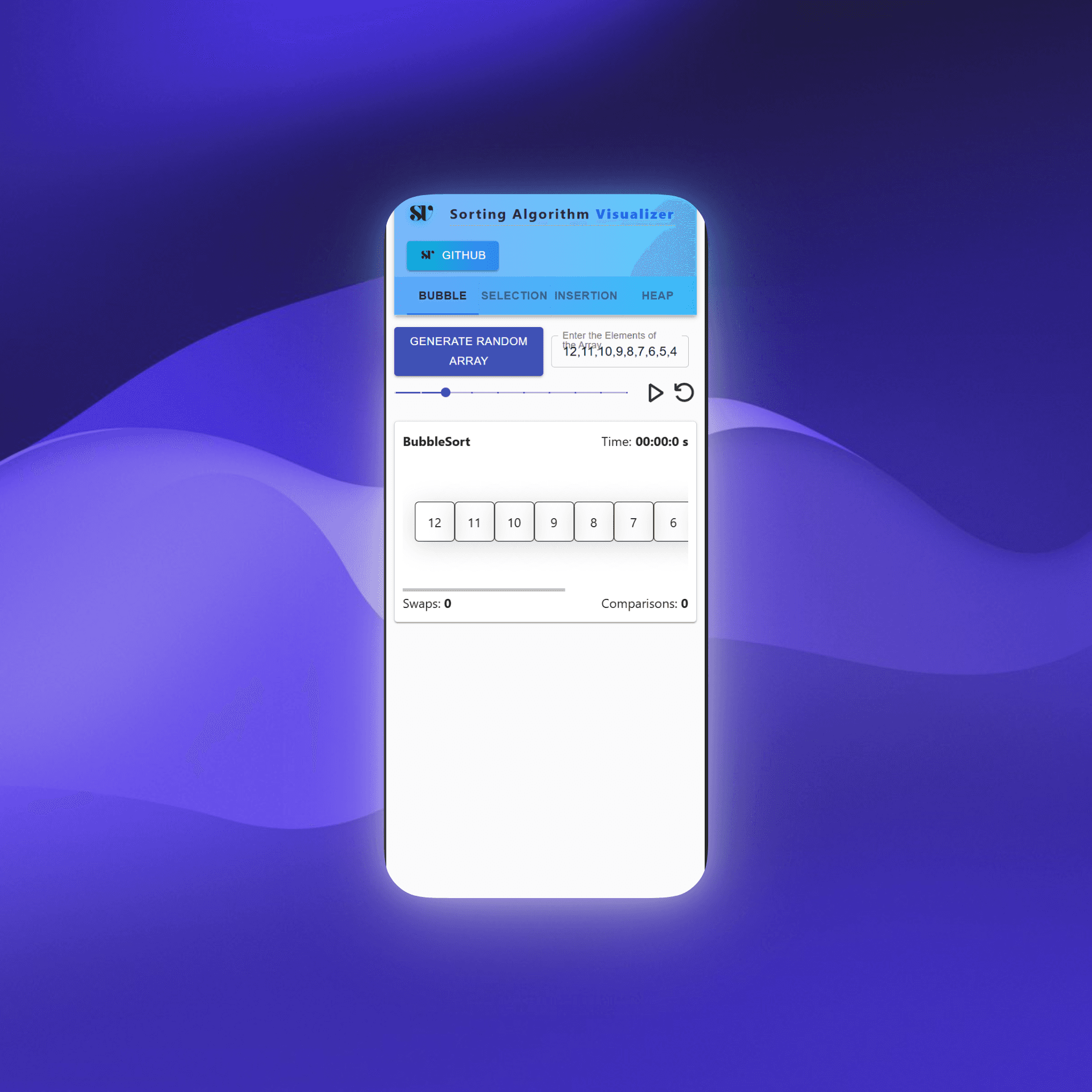
Why I Built This
When learning sorting algorithms, I could memorize that Quick Sort is O(n log n) but couldn't really see why it's faster than Bubble Sort's O(n²). I wanted to watch them work side by side, counting every comparison and swap.
This tool makes the invisible visible. You can pause mid-sort, see exactly which elements are being compared, and understand why some algorithms finish in 50 operations while others need 500.
Technical Challenges
- Pause/resume without desynchronization: Required careful state management to maintain exact execution position across animations
- Deterministic stepping for fair comparisons: Each algorithm needed to yield consistent steps for accurate side-by-side metrics
- Merge sort visualization model: Unlike swap-based algorithms, merge sort required a different approach to show auxiliary array operations
- Lightweight state management: Chose Zustand over Redux to avoid boilerplate while maintaining predictable state updates
- Animation fidelity vs. performance: Balanced smooth 60fps animations with accurate operation counting, especially on mobile devices
Features
Eight algorithms running side by side: Bubble, Selection, Insertion, Quick, Merge, Heap, Cocktail, and Comb Sort. Each tracks comparisons, swaps, and execution time.
You can adjust the array size (5-30 elements), control animation speed, pause mid-sort, and even input custom arrays to test edge cases.
How It Works
Each sorting algorithm is an async generator function that yields steps (compare, swap, mark sorted). This lets me pause/resume without losing position or desynchronizing animations.
I used Zustand for state management: one store for controls (speed, play/pause), another for data (array state, metrics). It's lighter than Redux and perfect for this kind of reactive UI.
Merge sort was tricky because it doesn't swap in place, it uses an auxiliary array. I had to build custom visualization logic just for it.
What I Learned
Async generators are perfect for step-by-step visualizations. Each algorithm yields its next move, which lets me pause/resume without any state management nightmares.
Animation synchronization is harder than it looks. Keeping the visual bars in sync with the logical algorithm state took careful timing and a lot of testing.
Not all algorithms fit the same visualization model. Most sorting algorithms just swap elements in place, but merge sort uses an auxiliary array, I had to completely rethink how to show that.